Manténgase sano!
192 Resultados de su búsqueda "Blood Pressure".
Resultados de noticias de salud - 192
Nearly 6 out of 10 U.S. women will have some type of heart disease during the next 25 years, a trend driven by rising rates of high blood pressure, a new American Heart Association report says.
Almost 60% of women could have high blood pressure by 2050, up from about 50% in 2020...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 25, 2026
- |
- Página completa
An ancient Chinese mind-body practice can lower a person’s blood pressure as well as medication or a program of brisk walking, a new study says.
Baduanjin is a widely practiced eight-movement sequence that combines slow, structured movement, deep breathing and meditation.<...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 19, 2026
- |
- Página completa
Doctors could reduce rates of a dangerous high blood pressure condition in pregnancy by taking one simple step, a new study says.
Prescribing daily aspirin to all pregnant women at their first prenatal visit was associated with an overall reduction in cases of severe preeclampsia, according to finding...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 13, 2026
- |
- Página completa
A new feature of the Apple Watch allows the device to passively track blood flow and notify users they might have high blood pressure.
However, folks who don’t receive such a warning from their smartwatch should not assume their blood pressure is healthy, a new study says....
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 10, 2026
- |
- Página completa
Four out of 5 American adults with high blood pressure don’t have their condition under control, putting them at increased risk for heart disease and dementia, a new study says.
About 79% of people with high blood pressure have failed to get it down to a healthier level, a...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 3, 2026
- |
- Página completa
People whose drinking water contains more salt have an increased risk of high blood pressure, a new evidence review says.
Particularly in coastal regions, salt in drinking water could be an overlooked contributor to elevated blood pressure, researchers reported recently in the j...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 30, 2026
- |
- Página completa
You might not notice a pinch of salt missing from your bread, sandwich or pizza, but your body definitely will, according to a pair of new European studies.
Efforts to lower sodium levels in packaged and prepared foods are expected to improve heart health in both France and the U.K., researchers write in the February issue of the journal
Treatment of high blood pressure is based on continual monitoring, with people checking their readings regularly and doctors steering their care based on those tests.
But many patients either can’t or won’t keep up with blood pressure monitoring at home, undermining ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 26, 2026
- |
- Página completa
Children might wind up with high blood pressure due to air pollution exposure that occurred in the womb or the cradle, a new study says.
Exposure to smog before and after birth increases a child’s odds of having higher blood pressure between ages 5 and 12, researchers repo...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 16, 2026
- |
- Página completa
Managing an expecting mother’s blood pressure could improve her odds of an overall healthy pregnancy, a new study says.
Just a 10-point increase in a pregnant woman’s systolic blood pressure — the top number in a blood pressure reading — is linked to an increased risk of many serious complications affecting both mother and baby, researchers reported Jan. 14 in the ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 15, 2026
- |
- Página completa
A widely used blood pressure medication is being pulled from shelves after testing suggested some batches may contain traces of other drugs.
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals has recalled several lots of bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets (sold under the brand name
A step as simple at sticking to the same bedtime each night could improve a person’s blood pressure, new research suggests.
In just two weeks, people whose more haphazard bedtimes shifted to a regular bedtime saw improvements in blood pressure that were equal to those seen when folks exercise more or cut down on salt intake, the study showed.
“This may be a s...
- Ernie Mundell HealthDay Reporter
- |
- November 26, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Black adults living in food deserts can beat high blood pressure, with a little help.
Folks living in an area with few grocery stores had a greater reduction in blood pressure if they participated in a program that home-delivered healthy eats, researchers recently reported in the
The rate of kids and teens with high blood pressure worldwide nearly doubled over the past two decades, according to a startling new report.
In 2020, more than 6% of children and adolescents under 19 had high blood pressure, up from around 3% in 2000, researchers reported Nov. 12 in The Lance...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- November 13, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Bribing folks with tickets to a cash lottery got them to take their blood pressure medicines more reliably, but did nothing to improve their health, a new study says.
Study participants were twice as likely to take their blood pressure medication when they could win a daily cash reward through a lottery, researchers reported Nov. 9 in the
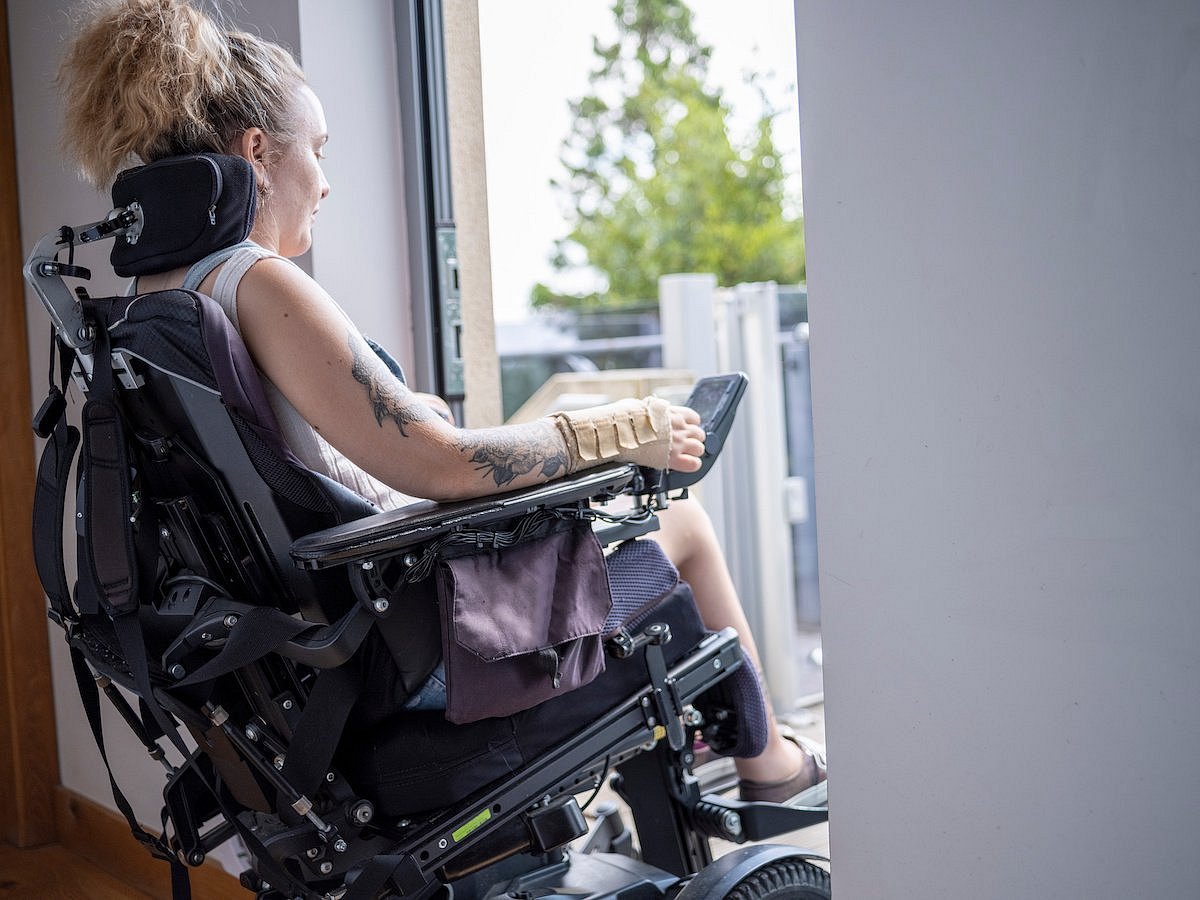
A spinal cord injury might be only the beginning of a person’s health woes, according to a new study.
People who’ve suffered spinal cord injuries are more likely to develop an array of chronic health problems, researchers reported Nov. 4 in
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recalled over half a million bottles of a widely prescribed blood pressure medication, prazosin hydrochloride, because of concerns about a potentially cancer-causing chemical.
New Jersey-based Teva Pharmaceuticals and drug distributor Amerisource Health Services initiated the voluntary recall for more...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- November 3, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Any boozing can cause your blood pressure to go up, a new study shows.
Even slight increases in alcohol consumption are associated with higher blood pressure, researchers reported Oct. 22 in the Journal of the American College of C...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 23, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Heart-related health problems might affect as many as 1 in 7 pregnancies, even among women without any prior heart disease, a new study says.
Researchers found a steady increase in heart-related health problems among more than 56,000 pregnancies between 2001 and 2019 in New Englan...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 9, 2025
- |
- Página completa
A recently approved injectable drug can significantly stall deteriorating health among people newly diagnosed with the most severe form of high blood pressure, a new study says.
Sotatercept reduced patient’s risk of ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 6, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Universal free meal programs appear to improve kids’ heart health, a new study says.
The proportion of students with high blood pressure fell by nearly 11% over five years among schools that signed up for free meal programs, researchers recently reported in
Immigrants come to the United States hale and healthy, but that doesn’t last long, a new study says.
Immigrants’ heart disease risk increases the longer they live in the U.S., according to research scheduled for presentation today at an American College of Cardiology meeting in Dubai.
Living in America takes its toll on immigrants’
Nearly everyone who suffers a heart attack, stroke or heart failure had at least one warning sign that cropped up years before, a new study says.
More than 99% of patients had one or more risk factors prior to their heart emergency, including high blood pressure, elevated ch...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 30, 2025
- |
- Página completa
People with spinal cord injuries sometimes suffer from blood pressure problems, as their brain loses the ability to manage the body’s blood pressure.
This leaves them vulnerable to blood pressure drops that cause fainting or spikes that put them at risk of a
People with fatty liver disease are more likely to die early if they have one of three additional health problems, a new study says.
High blood pressure, diabetes and low levels of “good” HDL cholesterol all increase the risk of death for people with fatty liver disease, res...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 19, 2025
- |
- Página completa
A common rheumatoid arthritis drug appears to also lower blood pressure, potentially reducing patients’ risk of heart disease, a new study says.
Methotrexate significantly lowered blood pressure compared to another arthritis drug called ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 9, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Folks figuring out how to take their blood pressure at home might be tempted to use online stock photos to see how it’s done — but they really shouldn’t, a new study warns.
Only about 1 in 7 stock photos found online correctly depict the right way to measure bl...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 9, 2025
- |
- Página completa
A novel pill that blocks the hormone aldosterone shows promise for lowering blood pressure and potentially delaying the progression of kidney disease in people with both conditions.
The preliminary findings were presented Saturday at an American Heart Association (AHA) mee...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 8, 2025
- |
- Página completa
A heart health journey may start much earlier than once thought, as new research shows that kids with higher blood pressure at age 7 had a sharply increased risk of dying of heart disease by their mid-50s.
The preliminary findings were presented Sunday at an American Heart Assoc...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 8, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Older adults managing high blood pressure might just have one more tool in the toolbox.
A new study suggests that artificial intelligence (AI)-powered voice agents can help older adults manage their high blood pressure, potentially transforming how remote patient care is d...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 8, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Most people with high blood pressure aren’t skipping the salt shaker in favor of a salt substitute, according to a new study.
Incredibly few Americans use salt substitutes, essentially waving aside a simple and effective way to manage their blood pressure, researchers repo...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 5, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Deaths from blood-pressure-driven kidney disease have increased dramatically during the past quarter-century, according to a new study.
Deaths from high blood pressure-related kidney disease increased by nearly half in the U.S. over the past 25 years, researchers reported Thursd...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 5, 2025
- |
- Página completa
An experimental pill might help people with stubborn high blood pressure that won’t relent to other treatments, clinical trial results show.
Patients with treatment-resistant high blood pressure saw a significant drop after taking the new drug baxdrostat once a day for three months, researc...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 4, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Everyone probably knows the phrase "music hath charms to soothe the savage breast," and new research suggests it may do the same for heart health.
A small study found that blood pressure appears to "synchronize" to patterns in music. British researchers say that might help boost the body's baroreflex sensitivity — its ability to regulate
Seniors with known heart-related problems aren’t doing a very good job taking steps to protect their health, a new study says.
Older folks with high blood pressure, stroke survivors and heart failure patients in the United States all have been neglecting Life’s Essen...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 20, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Tight control over blood pressure is not only good for patients, but is also cost-effective health care, a new study says.
Controlling blood pressure to below 120 systolic prevents more heart attacks, strokes, cases of heart failure and other heart-related health problems, compa...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 20, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Everyone’s seen the automatic blood pressure reader wedged unobtrusively into a corner of their local pharmacy.
These sit-down machines can pay huge dividends when it comes to helping people learn their heart health risks, a new study says.
Setting up these health stations at community ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 18, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Nearly half of U.S. adults should receive earlier treatment for high blood pressure, including lifestyle changes and medications, according to a set of new guidelines issued by America’s top heart health groups.
The guidelines call for early and more individualized treatme...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 15, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Folks fighting high blood pressure might receive some help from a household air purifier, a new study says.
Even in areas with relatively low air pollution levels, using a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) purifier at home might significantly lower a person’s blood pressu...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 12, 2025
- |
- Página completa
There’s a simple way older women can protect their heart health, a new study argues.
Just stand up.
Women who started standing up from a seated position more often during their day experienced notable improvement in blood pressure after three months, researchers reported recently in t...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 7, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Adding distance to your daily walk and picking up your pace can help reduce risk of heart problems associated with high blood pressure, a new study says.
Compared to a minimum step count of 2,300 steps, every 1,000 additional steps are associated with a 17% lower risk of heart att...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 7, 2025
- |
- Página completa
The time children and teens spend video gaming, scrolling through social media or watching TV could be putting their future heart health at risk, a new study says.
Each additional hour of screen time is associated with an increase in heart risk factors like blood pressure, c...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- August 6, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Doctors are regularly overlooking a common hormone-driven cause of high blood pressure, a new paper warns.
As many as 30% of high blood pressure patients seen by heart specialists and 14% of those seen in primary care have a condition called primary aldosteronism, researchers reported in the Jou...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- July 16, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Kids exposed to PFAS “forever chemicals” before birth have an increased risk of high blood pressure in childhood, particularly during their teen years, a new study says.
Teenage boys had a 17% higher risk of increased risk of elevated blood pressure if their moms had...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- June 13, 2025
- |
- Página completa
A good number of people don’t know that high blood pressure is a silent killer, increasing a person’s heart risk with no obvious symptoms, a new poll has found.
More than a third of Americans (37%) erroneously think high blood pressure always has noticeable symptoms ...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- June 12, 2025
- |
- Página completa
Being your own boss might seem potentially stressful, but self-employed women appear to have better heart health than those toiling for a company, a new study says.
Women working for themselves had lower rates of obesity, physical inactivity, poor diet and sleeplessness, researcher...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- June 3, 2025
- |
- Página completa
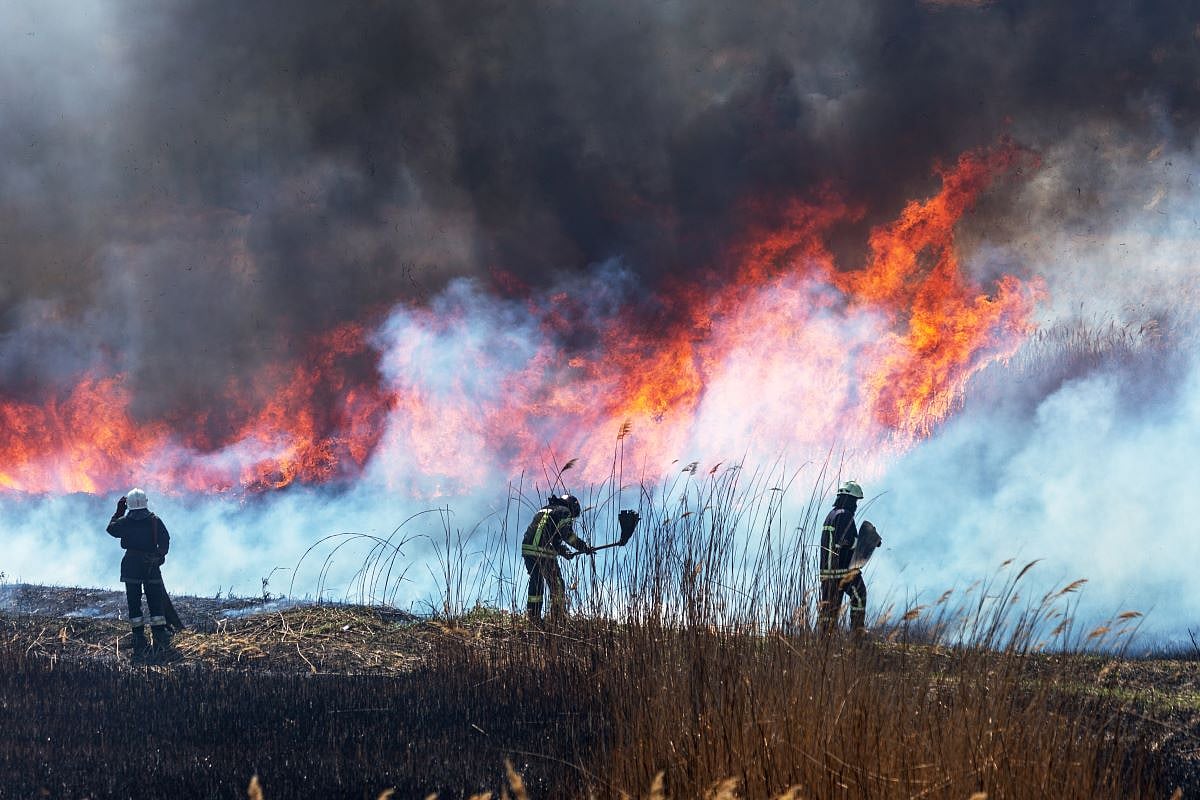
Skies choked with wildfire smoke can affect people’s heart and lung health for up to three months afterwards, a new study says.
The particle pollution created by wildfires continues to increase people’s risk of hospitalization for months after the smoke clears, researchers reported May 28 in the journal
Twice as many Americans now face the increased risk of death that comes from having both high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, a new study reports.
About 12% of the U.S. population had high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes at the same time in 2018, up from 6% in 1999, researchers reported recen...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 30, 2025
- |
- Página completa
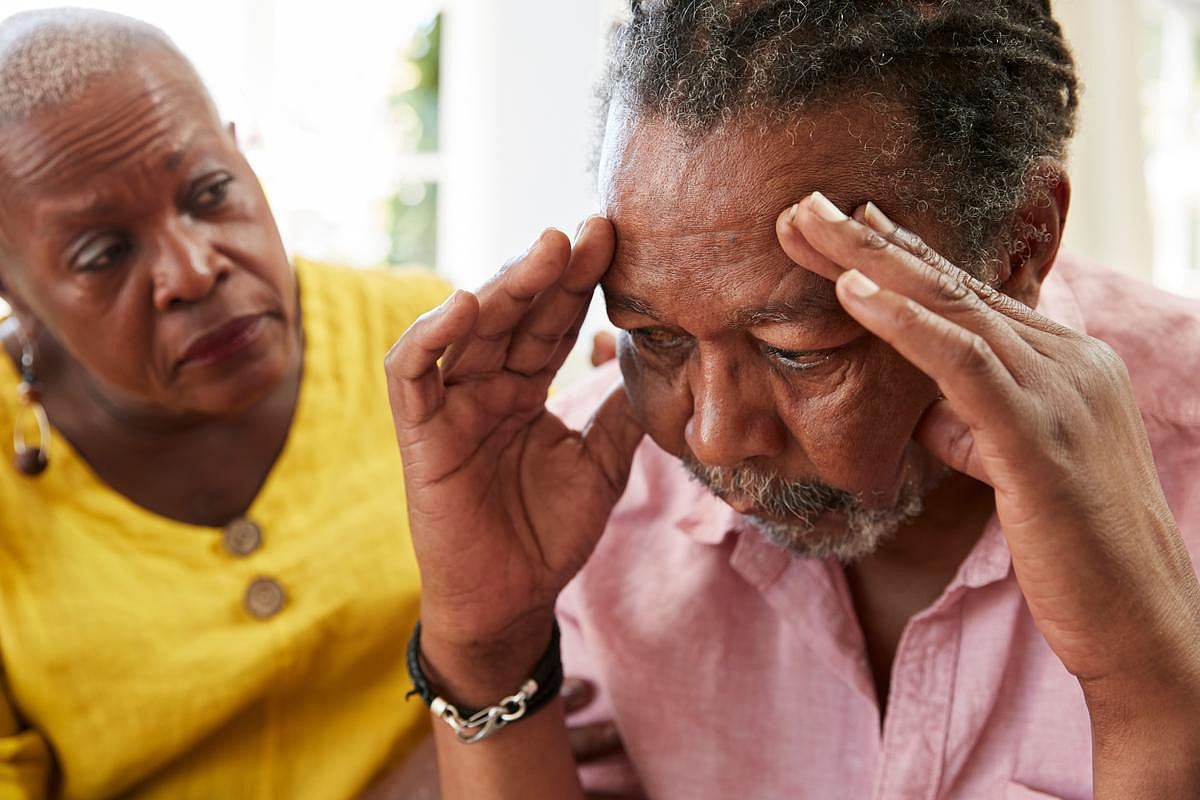
Heart disease, strokes and diabetes contribute to many dementia cases in the United States, but the risk is not equal everywhere, a new study says.
Overall, more than a third (37%) of U.S. dementia cases are linked to eight conditions: diabetes, heart failure, atrial fibril...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 29, 2025
- |
- Página completa
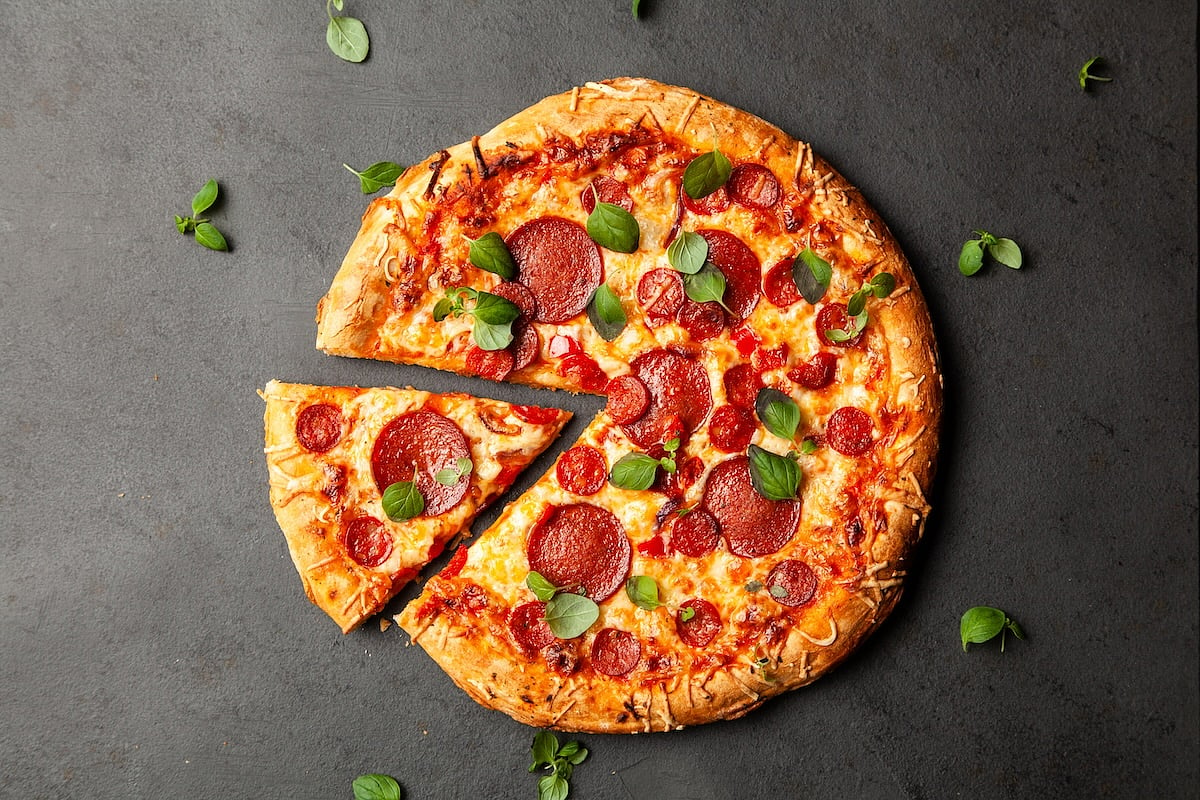
These days Americans can agree on few things, but unfortunately, pizza, soup and chicken aren’t among them, a new study says.
Those three foods are some of the main sources of sodium for Americans of all racial and ethnic groups, contributing to high blood pressure and hea...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 29, 2025
- |
- Página completa






















.jpg?w=1920&h=1080&mode=crop&crop=focalpoint)